并查集的概念
在计算机科学中,并查集(英文:Disjoint-set data structure,直译为不交集数据结构)是一种数据结构,用于处理一些不交集(Disjoint sets,一系列没有重复元素的集合)的合并及查询问题。并查集支持如下操作:
- 查询:查询某个元素属于哪个集合,通常是返回集合内的一个“代表元素”。这个操作是为了判断两个元素是否在同一个集合之中。
- 合并:将两个集合合并为一个。
- 添加:添加一个新集合,其中有一个新元素。添加操作不如查询和合并操作重要,常常被忽略。
理解下面三句话,并查集就学会了:
“并”的意思是把两个处在同一个连通分量的结点给并到一起.
“查”的意思是查找一个结点的根节点.
“并”的时候需要用到“查”
不过这样还是比较晦涩。下面我们用图片的方式来讲讲。
图解并查集
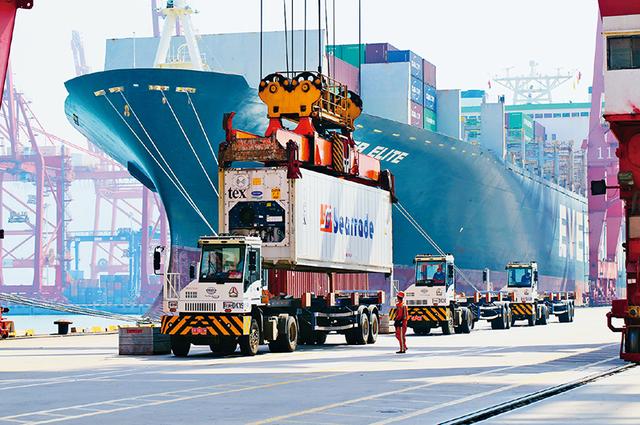
并查集的重要思想在于,用集合中的一个元素代表集合。
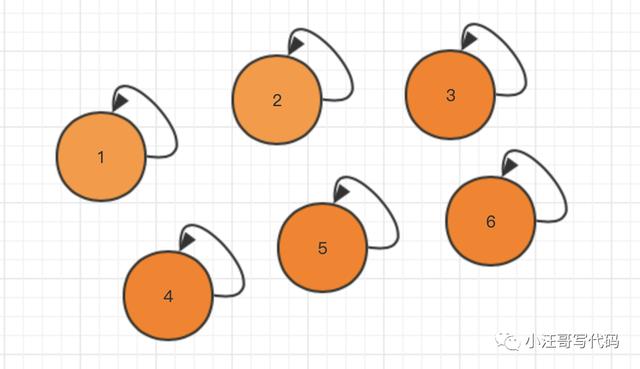
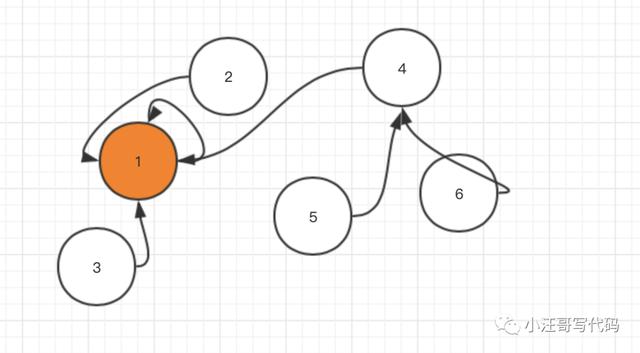
刚开始好比诸侯国,各自为政。
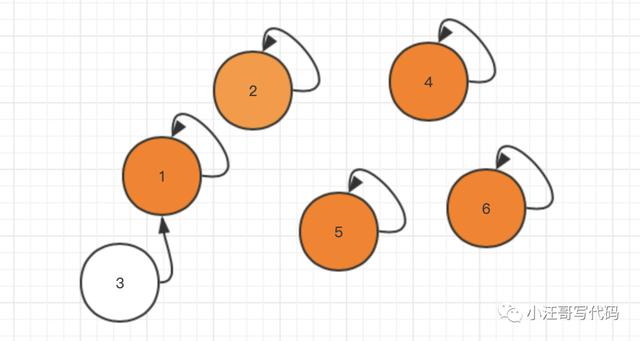
后来3号被1号吞并了,定都1号城池。
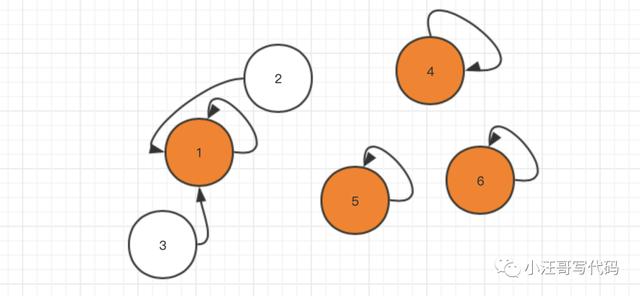
同时2号也被1号吞并了,定都1号城池。
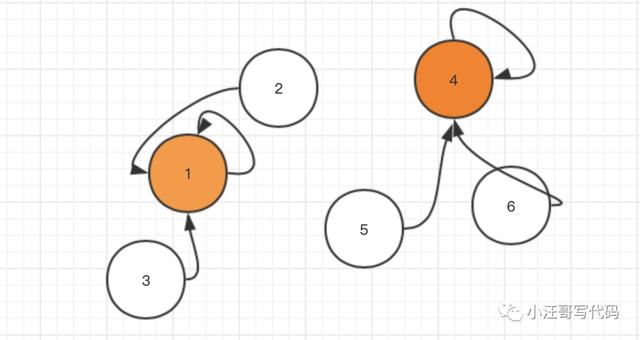
神州大地上 4,5,6也发生着相同的事情,5,6也背4号诸侯吞并了,定都4号城池。
后来1号把4号给吞并了,5,6也连带成了1号的领土。定都1号城池。

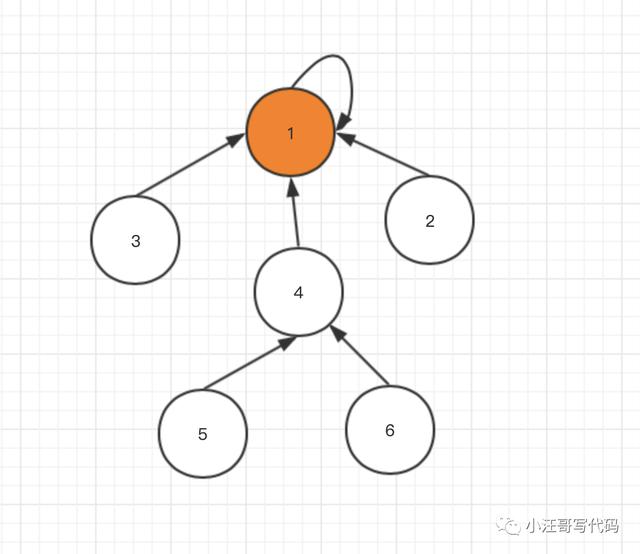
学习过前面的二叉树,其实我们可以把并查集想象成一个数的结构。
要寻找集合的代表元素(都城),只需要一层一层往上访问父节点(图中箭头所指的圆),直达树的根节点(图中橙色的圆)即可。
并查集实现代码
public static class Node<V> {
V value;
public Node(V v) {
value = v;
}
}
public static class UnionFind<V> {
public HashMap<V, Node<V>> nodes;//所有的节点
public HashMap<Node<V>, Node<V>> parents;// 每个节点的父几点
public HashMap<Node<V>, Integer> sizeMap;// 每个父节点有多少个孩子
public UnionFind(List<V> values) {
nodes = new HashMap<>();
parents = new HashMap<>();
sizeMap = new HashMap<>();
for (V cur : values) {
Node<V> node = new Node<>(cur);
nodes.put(cur, node);
parents.put(node, node);
sizeMap.put(node, 1);
}
}
// 给你一个节点,请你往上到不能再往上,把代表返回
public Node<V> findFather(Node<V> cur) {
Stack<Node<V>> path = new Stack<>();
while (cur != parents.get(cur)) {
path.push(cur);
cur = parents.get(cur);
}
while (!path.isEmpty()) {
//优化
parents.put(path.pop(), cur);
}
return cur;
}
//两个节点是不是在同一集合里
public boolean isSameSet(V a, V b) {
return findFather(nodes.get(a)) == findFather(nodes.get(b));
}
//合并两个节点
public void union(V a, V b) {
Node<V> aHead = findFather(nodes.get(a));
Node<V> bHead = findFather(nodes.get(b));
if (aHead != bHead) {
int aSetSize = sizeMap.get(aHead);
int bSetSize = sizeMap.get(bHead);
Node<V> big = aSetSize >= bSetSize ? aHead : bHead;
Node<V> small = big == aHead ? bHead : aHead;
//把数量少的节点挂在数据多的节点下面,可以避免路径过长
parents.put(small, big);
sizeMap.put(big, aSetSize + bSetSize);
sizeMap.remove(small);
}
}
public int sets() {
return sizeMap.size();
}
}
应用场景
leetcode朋友圈问题
https://leetcode.com/problems/friend-circles/
上面的并查集是HashMap用实现,常数时间比较长。下面我们用数组实现。数组直接寻址,速度比较快。
public static int findCircleNum(int[][] M) {
int N = M.length;
// {0} {1} {2} {N-1}
UnionFind unionFind = new UnionFind(N);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < N; j++) {
if (M[i][j] == 1) { // i和j互相认识
unionFind.union(i, j);
}
}
}
return unionFind.sets();
}
public static class UnionFind {
// parent[i] = k :i的父亲是k
private int[] parent;
// size[i] = k :如果i是代表节点,size[i]才有意义,否则无意义
// i所在的集合大小是多少
private int[] size;
// 辅助结构
private int[] help;
// 一共有多少个集合
private int sets;
public UnionFind(int N) {
parent = new int[N];
size = new int[N];
help = new int[N];
sets = N;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
size[i] = 1;
}
}
// 从i开始一直往上,往上到不能再往上,代表节点,返回
// 这个过程要做路径压缩
private int find(int i) {
int hi = 0;
while (i != parent[i]) {
help[hi++] = i;
i = parent[i];
}
for (hi--; hi >= 0; hi--) {
parent[help[hi]] = i;
}
return i;
}
public void union(int i, int j) {
int f1 = find(i);
int f2 = find(j);
if (f1 != f2) {
if (size[f1] >= size[f2]) {
size[f1] += size[f2];
parent[f2] = f1;
} else {
size[f2] += size[f1];
parent[f1] = f2;
}
sets--;
}
}
public int sets() {
return sets;
}
}
leetcode岛屿问题
https://leetcode.com/problems/number-of-islands/
1.感染法
public static int numIslands(char[][] board) {
int islands = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < board.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < board[0].length; j++) {
if (board[i][j] == '1') {
islands++;
infect(board, i, j);
}
}
}
return islands;
}
// 从(i,j)这个位置出发,把所有练成一片的'1'字符,变成0
public static void infect(char[][] board, int i, int j) {
if (i < 0 || i == board.length || j < 0 || j == board[0].length || board[i][j] != '1') {
return;
}
board[i][j] = 0;
infect(board, i - 1, j);
infect(board, i + 1, j);
infect(board, i, j - 1);
infect(board, i, j + 1);
}
2.并查集-hashmap
public static int numIslands1(char[][] board) {
int row = board.length;
int col = board[0].length;
Dot[][] dots = new Dot[row][col];
List<Dot> dotList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++) {
if (board[i][j] == '1') {
dots[i][j] = new Dot();
dotList.add(dots[i][j]);
}
}
}
UnionFind1<Dot> uf = new UnionFind1<>(dotList);
for (int j = 1; j < col; j++) {
// (0,j) (0,0)跳过了 (0,1) (0,2) (0,3)
if (board[0][j - 1] == '1' && board[0][j] == '1') {
uf.union(dots[0][j - 1], dots[0][j]);
}
}
for (int i = 1; i < row; i++) {
if (board[i - 1][0] == '1' && board[i][0] == '1') {
uf.union(dots[i - 1][0], dots[i][0]);
}
}
for (int i = 1; i < row; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < col; j++) {
if (board[i][j] == '1') {
if (board[i][j - 1] == '1') {
uf.union(dots[i][j - 1], dots[i][j]);
}
if (board[i - 1][j] == '1') {
uf.union(dots[i - 1][j], dots[i][j]);
}
}
}
}
return uf.sets();
}
public static class Dot {
//这里只是用了dot的内存地址
}
public static class Node<V> {
V value;
public Node(V v) {
value = v;
}
}
public static class UnionFind1<V> {
public HashMap<V, Node<V>> nodes;
public HashMap<Node<V>, Node<V>> parents;
public HashMap<Node<V>, Integer> sizeMap;
public UnionFind1(List<V> values) {
nodes = new HashMap<>();
parents = new HashMap<>();
sizeMap = new HashMap<>();
for (V cur : values) {
Node<V> node = new Node<>(cur);
nodes.put(cur, node);
parents.put(node, node);
sizeMap.put(node, 1);
}
}
public Node<V> findFather(Node<V> cur) {
Stack<Node<V>> path = new Stack<>();
while (cur != parents.get(cur)) {
path.push(cur);
cur = parents.get(cur);
}
while (!path.isEmpty()) {
parents.put(path.pop(), cur);
}
return cur;
}
public void union(V a, V b) {
Node<V> aHead = findFather(nodes.get(a));
Node<V> bHead = findFather(nodes.get(b));
if (aHead != bHead) {
int aSetSize = sizeMap.get(aHead);
int bSetSize = sizeMap.get(bHead);
Node<V> big = aSetSize >= bSetSize ? aHead : bHead;
Node<V> small = big == aHead ? bHead : aHead;
parents.put(small, big);
sizeMap.put(big, aSetSize + bSetSize);
sizeMap.remove(small);
}
}
public int sets() {
return sizeMap.size();
}
}
3.并查集-数组
public static int numIslands2(char[][] board) {
int row = board.length;
int col = board[0].length;
UnionFind2 uf = new UnionFind2(board);
for (int j = 1; j < col; j++) {
if (board[0][j - 1] == '1' && board[0][j] == '1') {
uf.union(0, j - 1, 0, j);
}
}
for (int i = 1; i < row; i++) {
if (board[i - 1][0] == '1' && board[i][0] == '1') {
uf.union(i - 1, 0, i, 0);
}
}
for (int i = 1; i < row; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < col; j++) {
if (board[i][j] == '1') {
if (board[i][j - 1] == '1') {
uf.union(i, j - 1, i, j);
}
if (board[i - 1][j] == '1') {
uf.union(i - 1, j, i, j);
}
}
}
}
return uf.sets();
}
public static class UnionFind2 {
private int[] parent;
private int[] size;
private int[] help;
private int col;
private int sets;
public UnionFind2(char[][] board) {
col = board[0].length;
sets = 0;
int row = board.length;
int len = row * col;
parent = new int[len];
size = new int[len];
help = new int[len];
for (int r = 0; r < row; r++) {
for (int c = 0; c < col; c++) {
if (board[r][c] == '1') {
int i = index(r, c);
parent[i] = i;
size[i] = 1;
sets++;
}
}
}
}
// (r,c) -> i
private int index(int r, int c) {
return r * col + c;
}
// 原始位置 -> 下标
private int find(int i) {
int hi = 0;
while (i != parent[i]) {
help[hi++] = i;
i = parent[i];
}
for (hi--; hi >= 0; hi--) {
parent[help[hi]] = i;
}
return i;
}
public void union(int r1, int c1, int r2, int c2) {
int i1 = index(r1, c1);
int i2 = index(r2, c2);
int f1 = find(i1);
int f2 = find(i2);
if (f1 != f2) {
if (size[f1] >= size[f2]) {
size[f1] += size[f2];
parent[f2] = f1;
} else {
size[f2] += size[f1];
parent[f1] = f2;
}
sets--;
}
}
public int sets() {
return sets;
}
}
leetcode岛屿问题二
https://leetcode.com/problems/number-of-islands-ii/
public static List<Integer> numIslands(int m, int n, int[][] positions) {
UnionFind1 uf = new UnionFind1(m, n);
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
for (int[] position : positions) {
ans.add(uf.connect(position[0], position[1]));
}
return ans;
}
public static class UnionFind1 {
private int[] parent;
private int[] size;
private int[] help;
private final int row;
private final int col;
private int sets;
public UnionFind1(int m, int n) {
row = m;
col = n;
sets = 0;
int len = row * col;
parent = new int[len];
size = new int[len];
help = new int[len];
}
private int index(int r, int c) {
return r * col + c;
}
private int find(int i) {
int hi = 0;
while (i != parent[i]) {
help[hi++] = i;
i = parent[i];
}
for (hi--; hi >= 0; hi--) {
parent[help[hi]] = i;
}
return i;
}
private void union(int r1, int c1, int r2, int c2) {
if (r1 < 0 || r1 == row || r2 < 0 || r2 == row || c1 < 0 || c1 == col || c2 < 0 || c2 == col) {
return;
}
int i1 = index(r1, c1);
int i2 = index(r2, c2);
if (size[i1] == 0 || size[i2] == 0) {
return;
}
int f1 = find(i1);
int f2 = find(i2);
if (f1 != f2) {
if (size[f1] >= size[f2]) {
size[f1] += size[f2];
parent[f2] = f1;
} else {
size[f2] += size[f1];
parent[f1] = f2;
}
sets--;
}
}
public int connect(int r, int c) {
int index = index(r, c);
if (size[index] == 0) {
parent[index] = index;
size[index] = 1;
sets++;
union(r - 1, c, r, c);
union(r + 1, c, r, c);
union(r, c - 1, r, c);
union(r, c + 1, r, c);
}
return sets;
}
}








